コレクション p(x) formula statistics 190834-How to calculate p(x) in statistics
P80 or P 80 = 80th percentile (Pk or P k = kth percentile) Defined here in Chapter 3 q = probability of failure on any one trial in binomial or geometric distribution, equal to (1−p) where p is the probability of success on any one trial Defined here in Chapter 6 Q1 or Q 1 = first quartile (Q3 or Q 3 = third quartile) Defined here inSo let's make a formula In our previous example, how can we get the values 1, 3, 3 and 1 ?T= x s x= p n (27) Con dence Interval = x t p s x n (28) TwoSample tstatistic t= x 1 x 2 s s2 1 n 1 s2 2 n 2 (29) Conf Interval = (x 1 x 2) t s s 2 1 n 1

Z Score Definition Calculation Interpretation Simply Psychology
How to calculate p(x) in statistics
How to calculate p(x) in statistics-Introduction to the Basic Practice of Statistics Ne w York WH Freeman & Co, 5th edition DESCRIPTIONS OF STATISTICS FORMULAS MEAN The mean, symbolized by xbar, equals one divided by the number of samples multiplied by the sum of all data points, symbolized by xsubiP(X = 2) = 3/8 ;



Continuous Probability Functions Introduction To Statistics
Formula Population Sample Size (n) = (Z 2 x P(1 P)) / e 2 Where, Z = Z Score of Confidence Level P = Expected Proportion e = Desired Precision N = Population Size For small populations n can be adjusted so that n(adj) = (Nxn)/(Nn) Related CalculatorStatistics is a branch of mathematics which deals with numbers and data analysisStatistics is the study of the collection, analysis, interpretation, presentation, and organization of data Statistical theory defines a statistic as a function of a sample where the function itself is independent of the sample's distributionP (X > 5) = P (X = 6 or X = 7 or X = 8) = P (X = 6) P (X = 7) P (X = 8) = 02 01 05 = 08
So it is essential to use the formula for a large number of data sets Here in calculating Poisson distribution, usually we will get the average number directly Based on the value of the λ, the Poisson graph can be unimodal or bimodal like below Step 4 x!/ (n x)!x!)p x q nx n The number of trials x The number of successes p The probability of success q The probability of failure (which is 1 p) The binomial distribution describes the behavior of a count of variable X if the following conditions apply 1 The number of observations n is fixedConditioning on the discrete level Example A fair coin is tossed 10 times;
˙ p np(1 p) (22) OneSample zstatistic To test H 0 = 0 usez= z 0 ˙= p n (23) Con dence Interval for = x z ˙ p n (24) Margin of Error ME= z ˙ p n (25) Minimum sample size n z ˙ ME 2 (26) OneSample tstatistic SEM= p s x n;The binomial formula is represented by the statistical formula as P (X=x)=b (x;n,P)= nCx * px (1p)nx The term 'n' represents the number of trials The term 'x' represents the number of successes in 'n' trials The term 'p' represents the probability of getting success from the 'n' binomial trialsThe pvalue, while it is one of the most widelyused and important concepts in statistics, is actually widely misunderstood Today we'll talk about what it is, and how to obtain it (If you're in a statistics class, or using this stuff out there in the real world, consider ordering "Statistics in Plain English" by Timothy Urdan


Properties Of Continuous Probability Density Functions Introductory Business Statistics



Probability Distribution
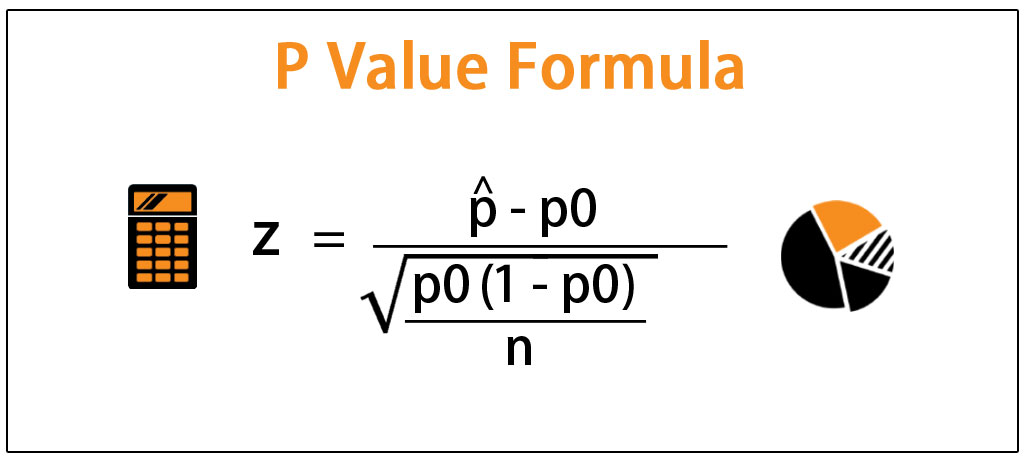
The pvalue, while it is one of the most widelyused and important concepts in statistics, is actually widely misunderstood Today we'll talk about what it is, and how to obtain it (If you're in a statistics class, or using this stuff out there in the real world, consider ordering "Statistics in Plain English" by Timothy UrdanThe probability of success (p) is 05 Do the calculation of binomial distribution to calculate the probability of getting exactly six successes Use the following data for the calculation of binomial distribution Calculation of binomial distribution can be done as follows, P (x=6) = 10 C 6 * (05) 6 (105) 106Pvalue Formula We Know that Pvalue is a statistical measure, that helps to determine whether the hypothesis is correct or not Pvalue is a number that lies between 0 and 1 The level of significance(α) is a predefined threshold that should be set by the researcher It is generally fixed as 005 The formula for the calculation for Pvalue is


Binomial Formula Explained



Sampling Distribution Of Sample Proportion Part 1 Video Khan Academy
Square root of one divided by the number of data points plus the mean of all x's squared, symbolized by xbar squared, divided by the sum of all x data points, symbolized by xsubI minus the mean of all x data points, symbolized by xbar, squaredFor our formula =TDIST (x, deg_freedom, tails) Here if we take x=t (test statistics), deg_freedom = n, tail = 1 or 2 Here as we can see the results, if we can see in percentages it's 272% Similarly, you can find the PValues for by this method when values of x, n, and tails are providedP(X= k) = n k pk(1 p)n k (21) =np;


P Value Formula Step By Step Examples To Calculate P Value



Beta Distribution Intuition Examples And Derivation By Aerin Kim Towards Data Science
Hypergeometric formula P(X = x) = h(x;P′ = x / n where x represents the number of successes and n represents the sample size The variable p′ is the sample proportion and serves as the point estimate for the true population proportion q′ = 1 – p′ p ′ ~ N (p, p q n) p ′ ~ N (p, p q n) The variable p′ has a binomial distribution that can be approximated with the normal distribution shown hereGetting up to x successes in n trials, when p is the probability of success in 1 trial) IMPORTANT there are variations on this one, which we will talk about Be sure to get them clear in your mind At most/less than or equal to ≤ binomcdf(n,p,x) Less than < binomcdf(n,p,x1) At least/greater than or equal to ≥ 1 minus binomcdf(n,p,x1)


Negative Binomial Experiment Distribution Definition Examples Statistics How To
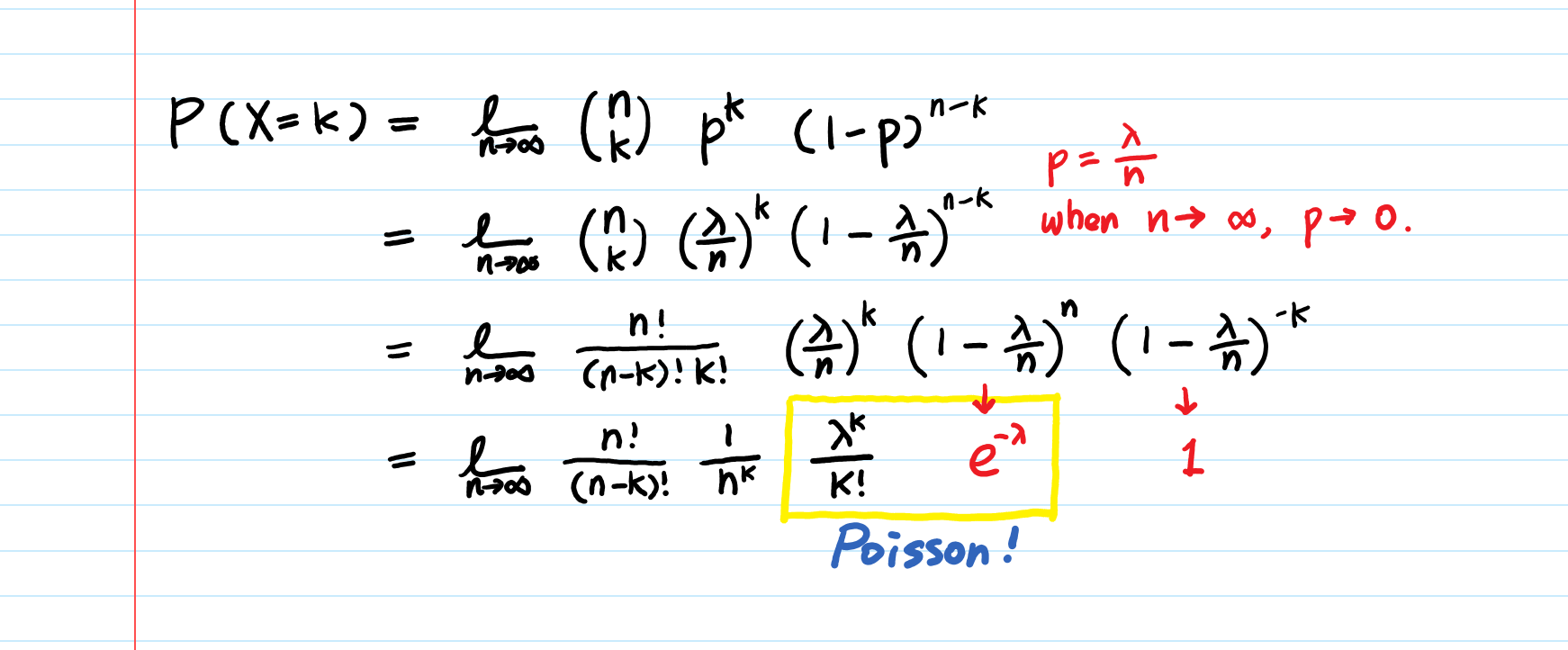


Poisson Distribution Explained Intuition Examples And Derivation Towards Data Science
The above formula shows us that P(M ∩ F) = P( MF ) x P( F ) The probability that a female is selected is P( F ) = 280/400 = 70% The conditional probability that the student selected is enrolled in a mathematics course, given that a female has been selected is P( MF ) = 80% We multiply these probabilities together and see that we have an 80% x 70% = 56% probability of selecting a female student who is enrolled in a mathematics courseAnd this is what it looks like as a graph It is symmetrical!Frequently Used Statistics Formulas and Tables Chapter 2 highest value lowest value x x n x N wx x w f x x f Note textbooks and formula sheets interchange "r" and "x" for number of successes Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions 22



Calculating A P Value Given A Z Statistic Video Khan Academy
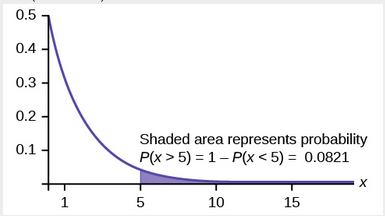


The Exponential Distribution Introduction To Statistics
P(X = 1) = 3/8 ;The z formula confirms this z = (x – mean)/std dev z = (78 – )/ 4 = 4/4 = 1 So, the z value for 78 is 1 This tells us that P( 74 < x < 78) is the same exact thing as P(2 < z < 1) Using the z table, we will need to do two things IMPORTANT NOTE the z table is cumulative and always starts on the left So the P(z < 1) is 1587In his influential book Statistical Methods for Research Workers (1925), Fisher proposed the level p = 005, or a 1 in chance of being exceeded by chance, as a limit for statistical significance, and applied this to a normal distribution (as a twotailed test), thus yielding the rule of two standard deviations (on a normal distribution) for statistical significance (see 68–95–997 rule)



Variance Wikipedia


The Binomial Distribution
EBP is error bound for the proportion p′ = x n p ′ = x n p′ = the estimated proportion of successes ( p′ is a point estimate for p, the true proportion) x = the number of successes n = the size of the sample The error bound for a proportion is EBP = (zα 2)(√p′q′ n) ( z α 2) ( p ′ q ′ n) where q' = 1p'N, P) = nCx * Px * (1 – P)n – x Where b = binomial probability x = total number of "successes" (fail or pass, tails or heads, etc) P = probability of success on an individual experiment n = number of experiment There is another formula to write it that is a slightly different way that isFrequently Used Statistics Formulas and Tables Chapter 2 highest value lowest value x x n x N wx x w f x x f Note textbooks and formula sheets interchange "r" and "x" for number of successes Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions 22



The Z Score Formula For Standard Bell Curves P Value Standard Deviation Data Science Learning



Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
The standard notation is to use a lower case letter to represent an actual event, and an upper case letter for the Random Variable used to measure the probability of the event occurring Thus the correct table would be And then;If a discrete random variable X has the following probability density function (pdf), it is said to have a binomial distribution P(X = x) = n C x q (nx) p x, where q = 1 p p can be considered as the probability of a success, and q the probability of a failureThe probability of success is given by the geometric distribution formula P ( X = x) = p × q x − 1 Where − p = 30 % = 03 x = 5 = the number of failures before a success Therefore, the required probability P ( X = 5) = 03 × ( 1 − 03) 5 − 1, = 03 × ( 07) 4, ≈ 0072 ≈ 72 % Previous Page Print Page


Binomial Formula Explained


A New Formula Sheet For The Ap Statistics Exam
(q = 1 p) P(x)= probability of getting exactly x success among n trials Be sure that xand p both refer to the same category being called a successP(X = 3) = 1/8 ;/ (n x)!x!)p x q nx n The number of trials x The number of successes p The probability of success q The probability of failure (which is 1 p) The binomial distribution describes the behavior of a count of variable X if the following conditions apply 1 The number of observations n is fixed


4 2 Discrete Random Variables Probability Mass Functions An Introduction To Probability And Simulation



Z Score Definition Calculation Interpretation Simply Psychology
The random variable X is the number of heads in these 10 tosses, and Y — the number of heads in the first 3 tosses In spite of the fact that Y emerges before X it may happen that someone knows X but not Y Conditional probabilityFor our formula =TDIST(x, deg_freedom, tails) Here if we take x=t (test statistics), deg_freedom = n, tail = 1 or 2 Here as we can see the results, if we can see in percentages it's 272% Similarly, you can find the PValues for by this method when values of x, n, and tails are providedP(X = 1) = 1/6, P(X = 2) = 1/6, etc So E(X 2) = 1/6 4/6 9/6 16/6 25/6 36/6 = 91/6 = The expected value of a constant is just the constant, so for example E(1) = 1 Multiplying a random variable by a constant multiplies the expected value by that constant, so E2X = 2EX A useful formula, where a and b are constants, is



Continuous Probability Functions Introduction To Statistics
/JointProbabilityDefinition2-fb8b207be3164845b0d8706fe9c73b01.png)


Joint Probability Definition
Binommial Distribution Formula P(x) = (n!$$ P(4) = \frac{6!}{4!(64)!} \cdot 065^4 \cdot (1065)^{64} $$ Evaluating the expression, we have $$ P(4) = $$ Complete Binomial Distribution Table If we apply the binomial probability formula, or a calculator's binomial probability distribution (PDF) function, to all possible values of X for 6 trials, we can construct aThis calculator will compute cumulative probabilities for a binomial outcome, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring For the number of successes x, the calculator will return P (Xx), and P (X≥x) Please enter the necessary parameter values, and then click 'Calculate'



Content Probability Functions


Binomial Distribution Video Khan Academy
P(X < 1) = P(X = 0) P(X = 1) = 025 050 = 075 Like a probability distribution, a cumulative probability distribution can be represented by a table or an equation In the table below, the cumulative probability refers to the probability than the random variable X is less than or equal to xIs the Factorial of actual events happened x Below is an example of how to calculateP(X = 0) = 1/8 ;



Engineering Statistics Lab 2 Chapter 3 Material Using Minitab To Plot Frequency Distribution And Calculate Mea Homeworklib
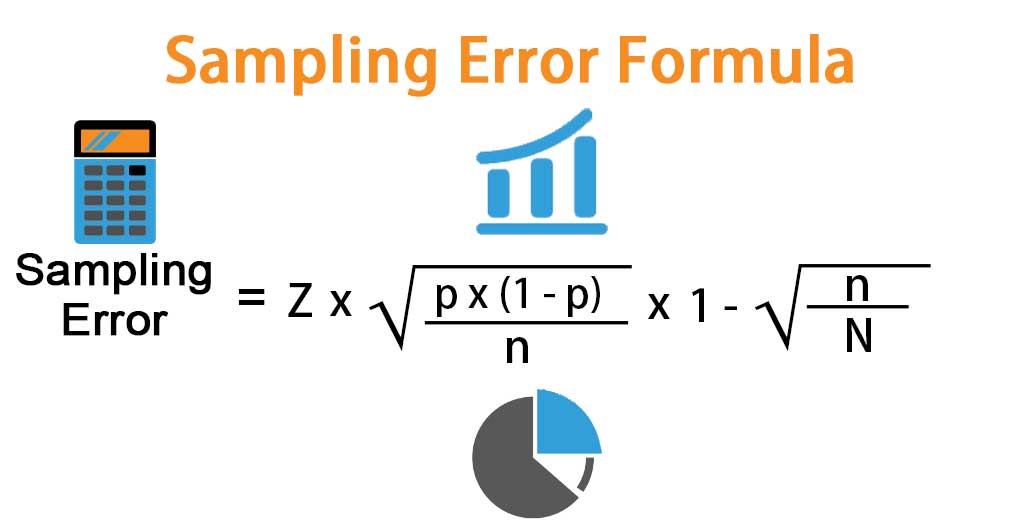


Sampling Error Formula Calculator Example With Excel Template
Pvalue Formula We Know that Pvalue is a statistical measure, that helps to determine whether the hypothesis is correct or not Pvalue is a number that lies between 0 and 1 The level of significance(α) is a predefined threshold that should be set by the researcher It is generally fixed as 005 The formula for the calculation for Pvalue isThis calculator will compute the probability of an individual binomial outcome (ie, a binomial probability), given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurringMaking a Formula Now imagine we want the chances of 5 heads in 9 tosses to list all 512 outcomes will take a long time!


4 1 Probability Density Functions Pdfs And Cumulative Distribution Functions Cdfs For Continuous Random Variables Statistics Libretexts


The Binomial Distribution
This proves that the sample proportion is an unbiased estimator of the population proportion p The variance of X/n is equal to the variance of X divided by n², or (np(1p))/n² = (p(1p))/n This formula indicates that as the size of the sample increases, the variance decreasesBinommial Distribution Formula P(x) = (n!In probability and statistics distribution is a characteristic of a random variable which is the probability of random variable X to get value smaller than or equal to x F(x) = P(X ≤ x) Continuous distribution The cumulative distribution function F(x) is calculated by integration of the probability density function f(u) of continuous



Normal Approximation To The Binomial Statistics How To



Lecture Notes Lecture Formula Sheet Studocu
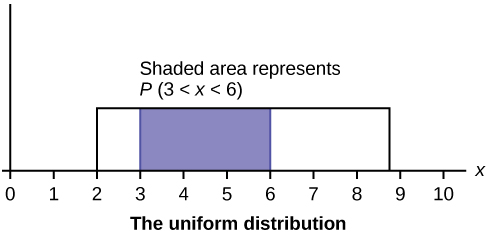
This calculator will compute cumulative probabilities for a binomial outcome, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring For the number of successes x, the calculator will return P(Xx), and P(X≥x)Calculate the rank r for the percentile p you want to find r = (p/100) * (n 1) 1 If r is an integer then the data value at location r, x r, is the percentile p p = x rLabel the graph with f(x) and xScale the x and y axes with the maximum x and y valuesf(x) = latex\displaystyle\frac{{1}}{{}}/latex, latex0{\leq}x{\leq}/latex To calculate the probability that x is between two values, look at the following graph Shade the region between latexx=23/latex and latexx=127/latex Then calculate the shaded area of a rectangle
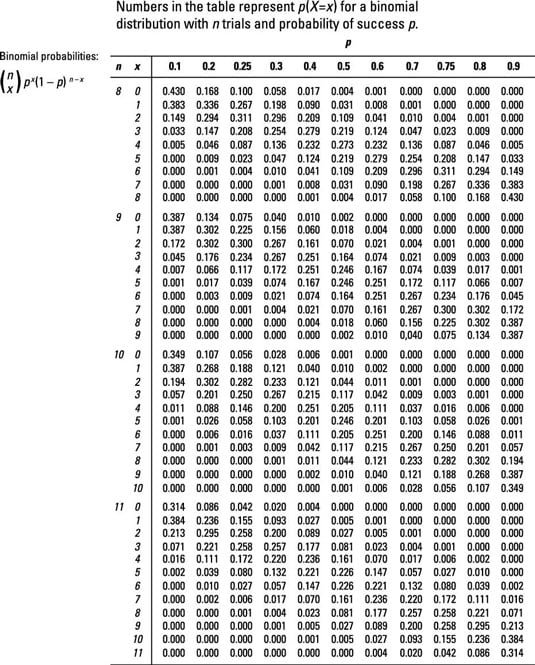


Figuring Binomial Probabilities Using The Binomial Table Dummies



Read More About Binomial Distribution Examples Binomial Distribution Data Science Data Science Statistics
Method 1 Use formula √E((Xμ)2) x P(X=x) xμ (xμ)2 19 04 06 036 5 03 134 27 02 86 7396 39 01 6 E(X) = 184 (ie μ) E((xμ)2) = σ = √ =N, n, k) = k C x Nk C nx / N C n Mean of hypergeometric distribution = μ x = n * k / N Variance of hypergeometric distribution = σ x 2 = n * k * ( N k ) * ( N n ) / N 2 * ( N 1 )If a discrete random variable X has the following probability density function (pdf), it is said to have a binomial distribution P(X = x) = n C x q (nx) p x, where q = 1 p p can be considered as the probability of a success, and q the probability of a failure
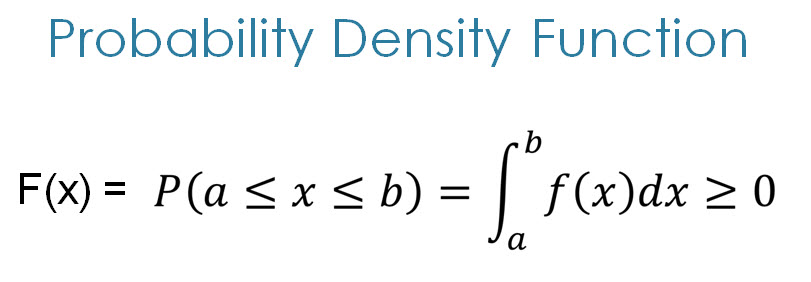


Continuous Probability Distributions Env710 Statistics Review Website
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/conditional-56edf9de5f9b5867a1c1924c.jpg)


Use Conditional Probability To Calculate Intersections
X P(X=x) xμ (xμ)2 19 04 06 036 5 03 134 27 02 86 7396 39 01 6 E(X) = 184 (ie μ) E((xμ)2) = σ = √ = Calculating (example continued) Method 2 Use formula √(E(X2)



Copyright C 1998 Triola Elementary Statistics Addison Wesley Longman 1 Binomial Experiments Section 4 3 Section 4 4 M A R I O F T R I O L A Copyright Ppt Download



Formulas Binomial Distribution P X Cip Q W Chegg Com



Solved Let X Uniform 1 2 N I E P X K Find Chegg Com



Solved Page 4 Of 7 Statistics Assignment Binomial Problem Chegg Com



Ap Statistics Chapter 8 Binomial And



Solution To Practice Midterm 2 Department Of Statistics And



Expected Value In Statistics Definition And Calculations



Poisson Distribution Equation The Statistics Matrix Photographic Print By Markcstansberry Redbubble



Expected Value And Variance Of Discrete Random Variables Youtube



Expected Value Wikipedia
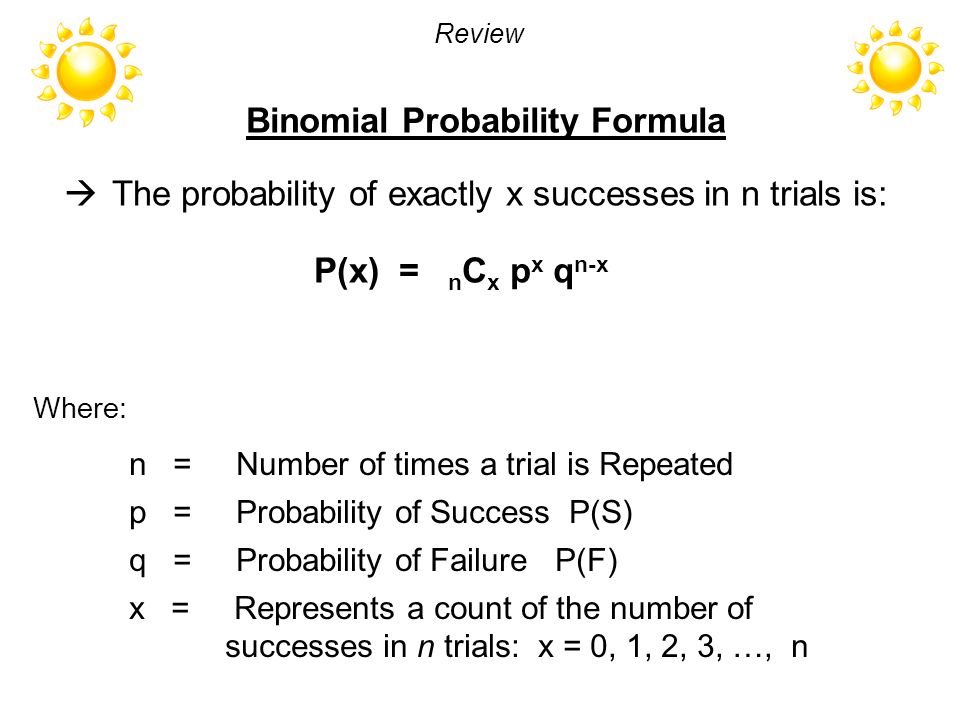


Teacher Introductory Statistics Lesson 4 2 B Objective Ppt Video Online Download



1 3 6 6 18 Binomial Distribution
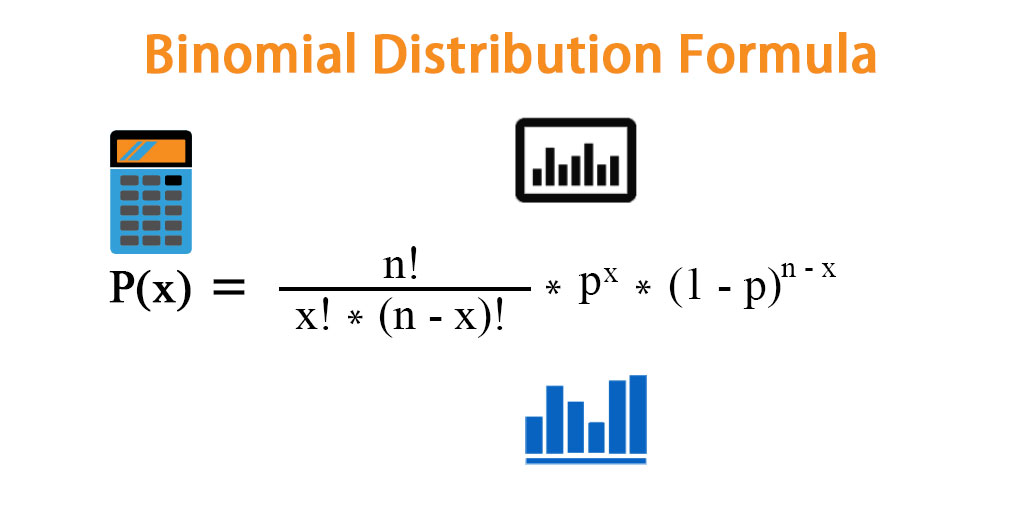


Binomial Distribution Formula Calculator Excel Template
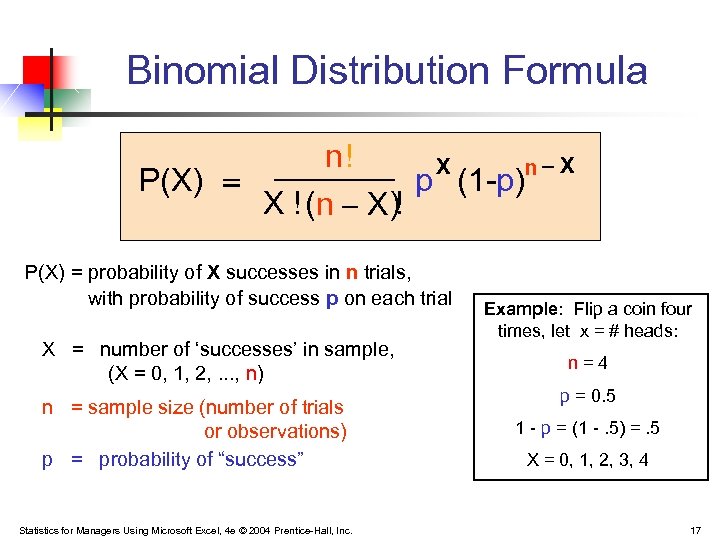


Statistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel 4 Th



Chapter 6 Stats Diagram Quizlet



Formulas Statistics



Statistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel 5th Edition Ppt Video Online Download



Lmdsnznhxqe Tm



Mean Expected Value Of A Discrete Random Variable Video Khan Academy
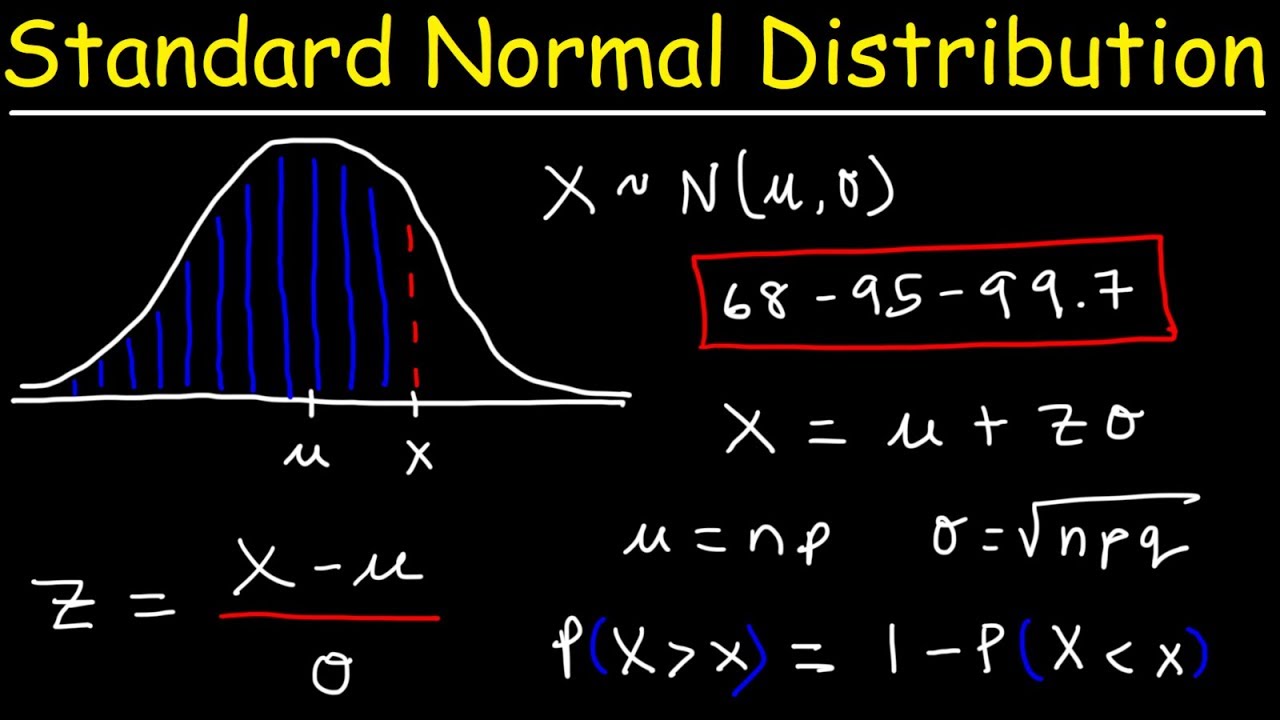


Standard Normal Distribution Tables Z Scores Probability Empirical Rule Stats Youtube



Ap Statistics



Statistical Inference Formulasheet
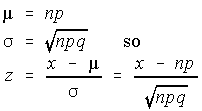


Stats Estimating The Proportion



A Simple Explanation Of Continuity Correction In Statistics Statology
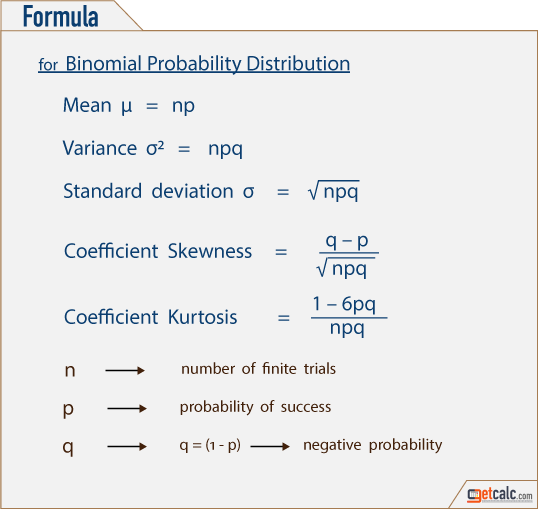


Binomial Distribution Formulas Calculator



Solved Solve The Following Problems By Using The Binomial Chegg Com



Guide To Binomial Distribution Formula Here We Discuss How To Calculate Probability Of X Using Binomial Distributio Binomial Distribution Formula Data Science
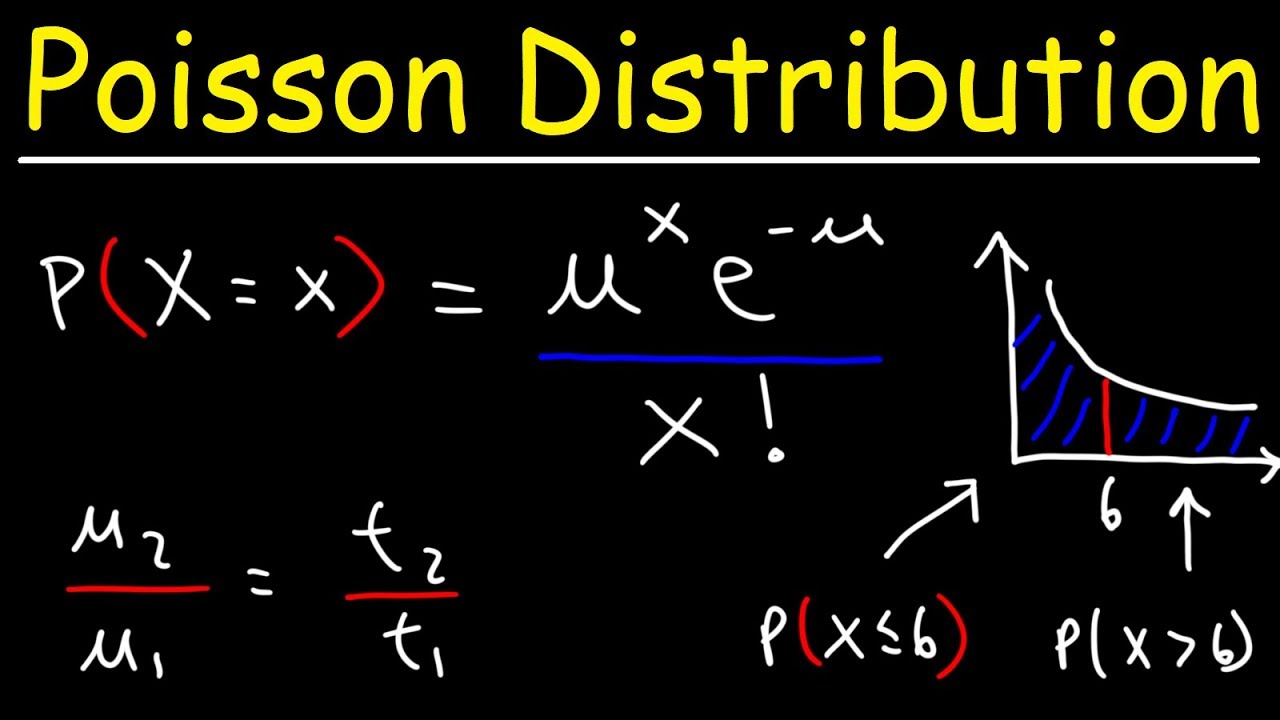


Introduction To Poisson Distribution Probability Statistics Youtube



Continuous Probability Functions Introduction To Statistics



Math 1600 Section 1 Fall 10 A Statistics Midterm 2 Review Sheet



Formulas Statistics


Expected Value In Statistics Definition And Calculations
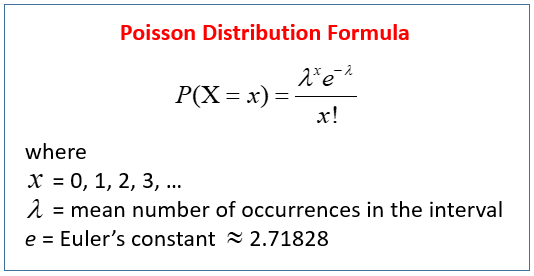


Poisson Distribution Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
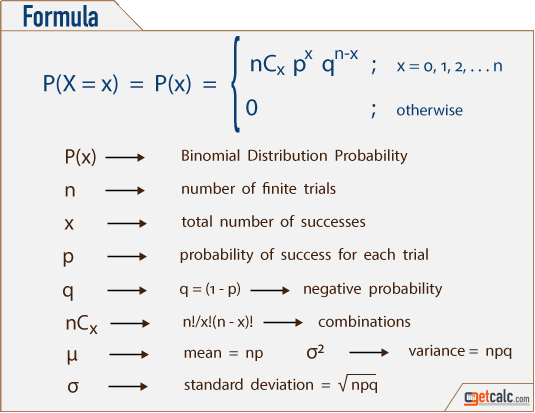


Binomial Distribution Formulas Calculator



How To Find An Expected Value Youtube
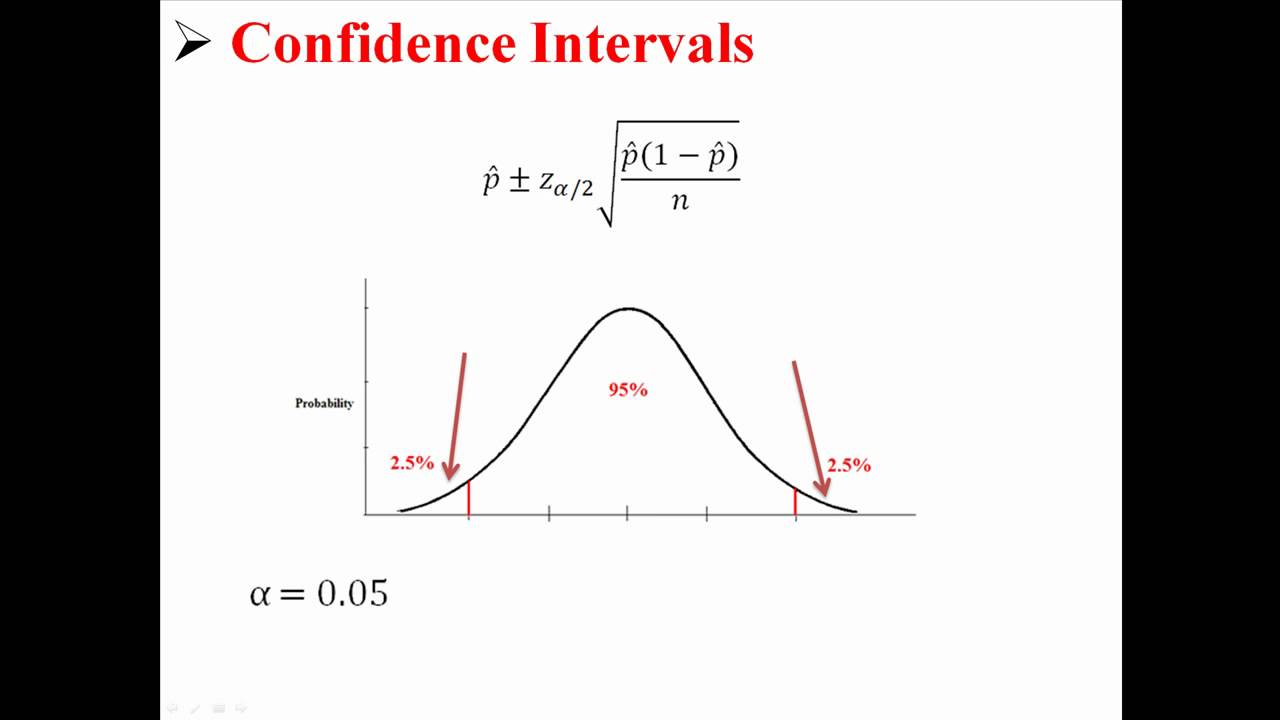


A Population Proportion Introduction To Statistics



Order Statistic Wikipedia
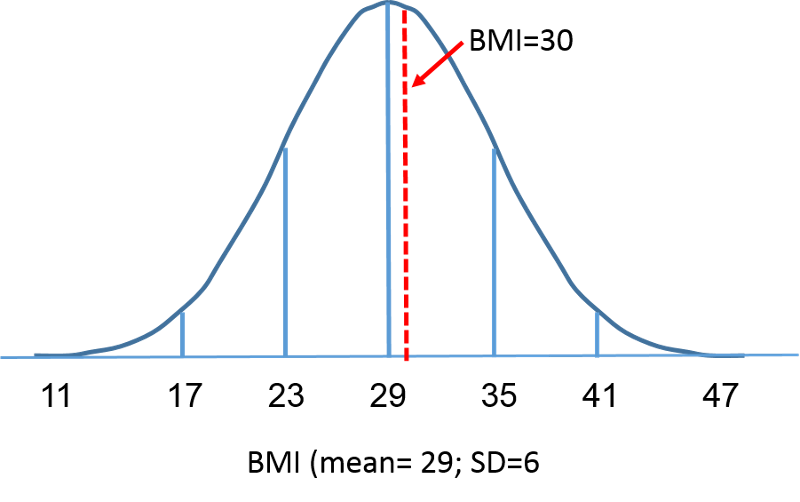


The Standard Normal Distribution



Variance Wikipedia


Order Statistics 10 30



Stats Chapter 8
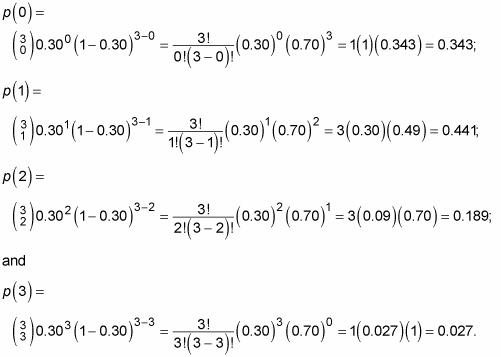


How To Find Binomial Probabilities Using A Statistical Formula Dummies


The Binomial Distribution
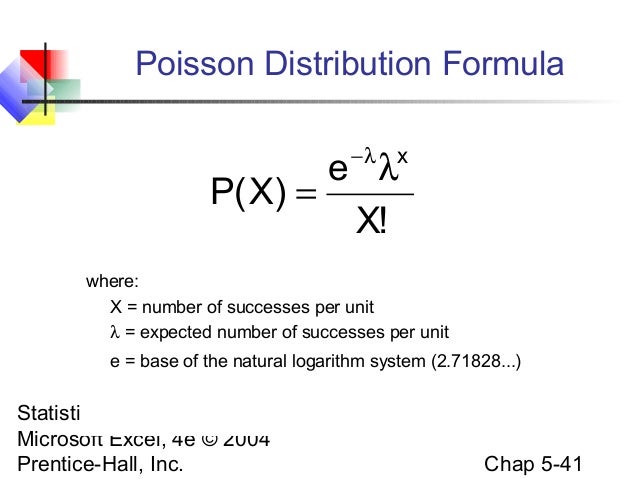


Chap05 Discrete Probability Distributions



Z Or Standard Score Value Calculator Standard Deviation Statistics Math Math Formulas


Binomial Distribution Video Khan Academy
/complement-56a8fa9a5f9b58b7d0f6e9e7.jpg)


How To Use The Complement Rule In Statistics
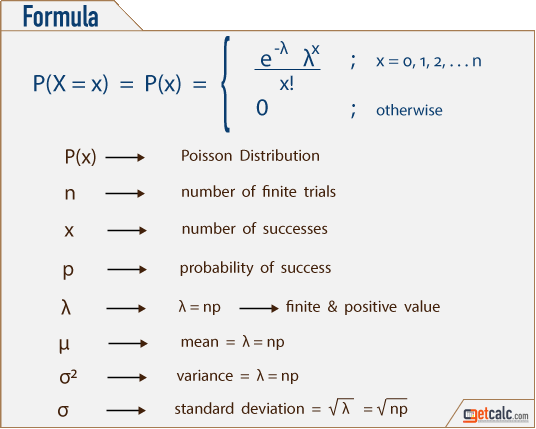


Poisson Distribution Calculator Formula Examples



Probabilty Statistics Formula Review 2 Txt Probability Formula Review Free Quick Notes Books Has Your Copies Of Types And Characteristics Course Hero
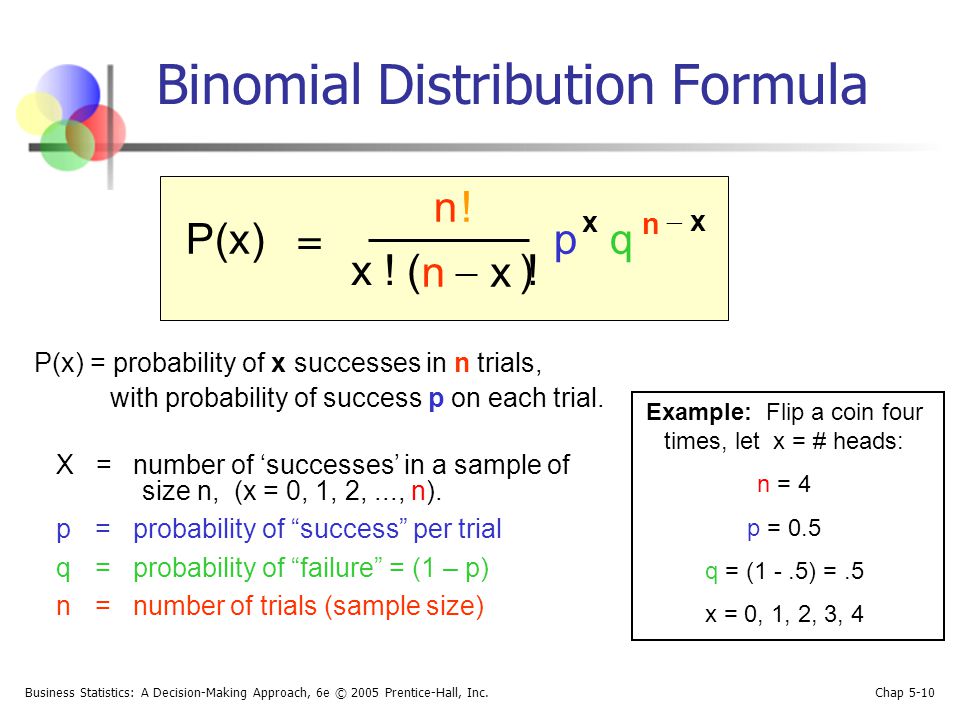


Chapter 5 Discrete And Continuous Probability Distributions Ppt Download
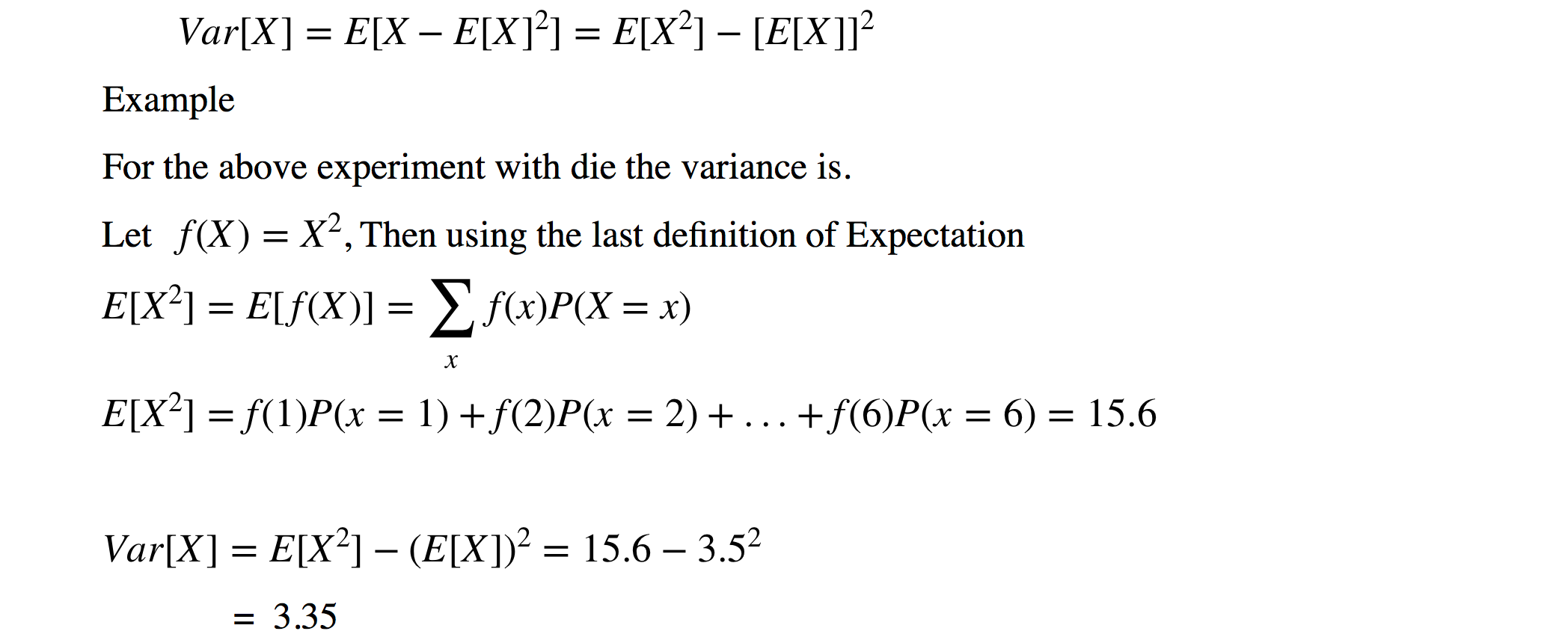


Basic Probability Theory And Statistics By Parag Radke Towards Data Science



Using The Normal Distribution Mgmt 2262 Applied Business Statistics Openstax Cnx



Order Statistic Wikipedia



Binomial Probabilities On The Ti Or 84 Calculator Mathbootcamps



Solved Gbus280 Business Statistics Practice 3 Makeup Name Chegg Com


A Biologist S Guide To Statistical Thinking And Analysis
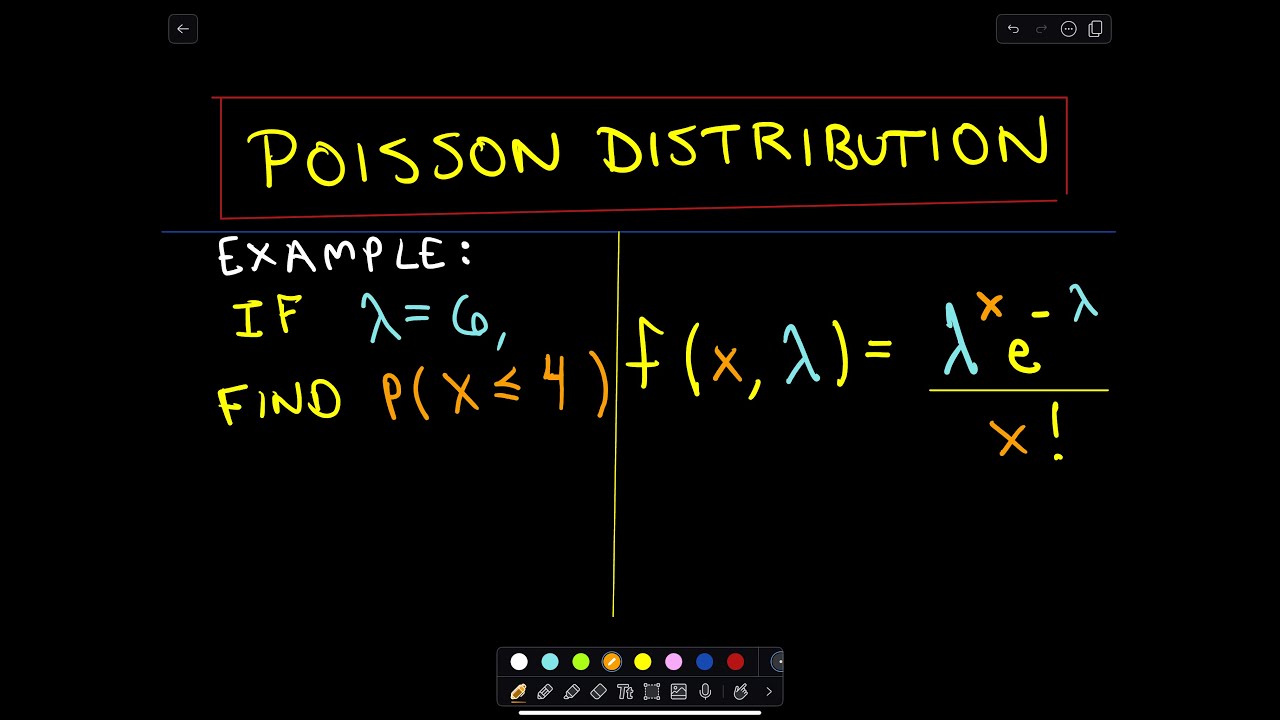


The Poisson Distribution Youtube
/FormulaForExpectedValue-58b8980d3df78c353cc32aff.jpg)


The Formula For Expected Value
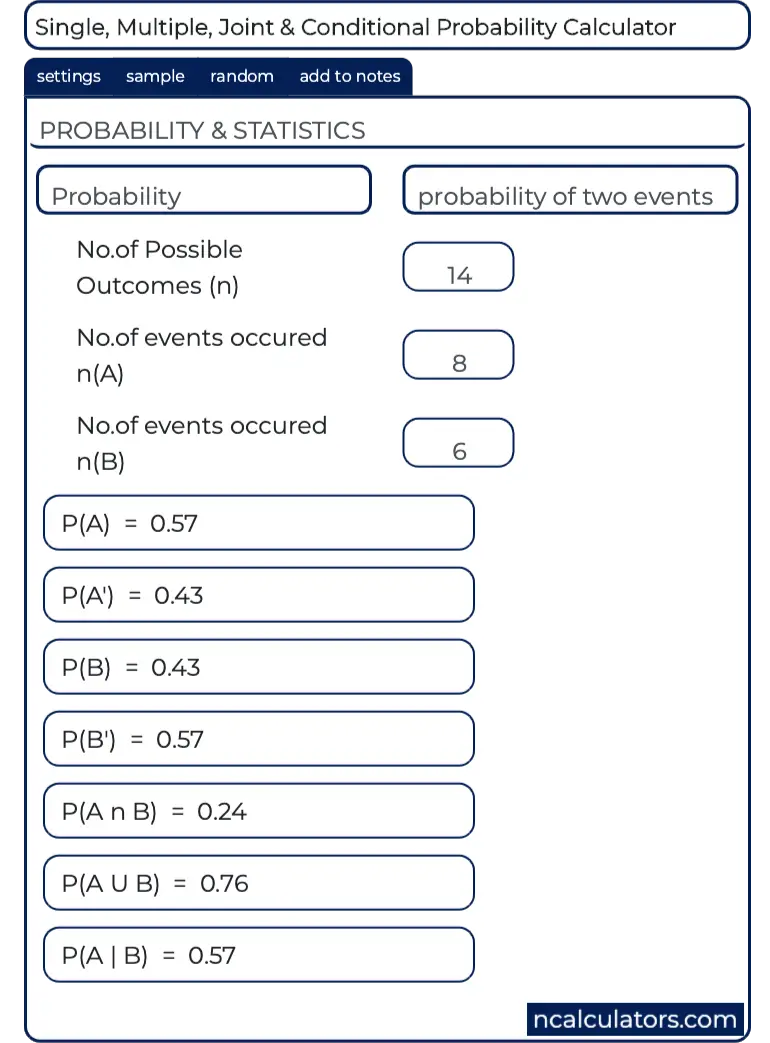


Probability Calculator
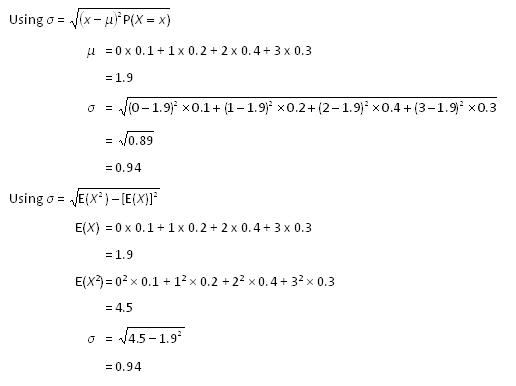


Standard Deviation Of A Discrete Random Variable Nz Maths
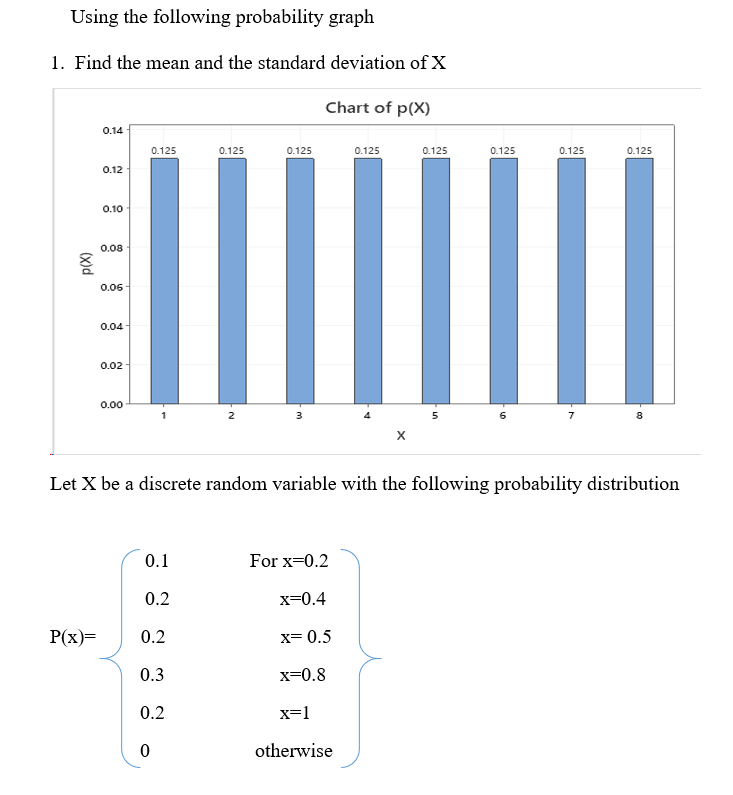


Solved Find The Range Of Values Of X Find P X 0 8 Find Chegg Com


コメント
コメントを投稿